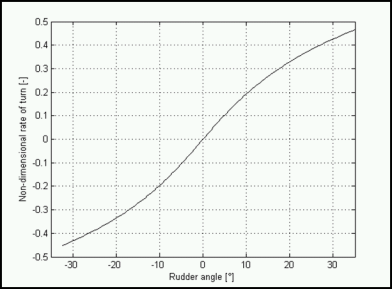
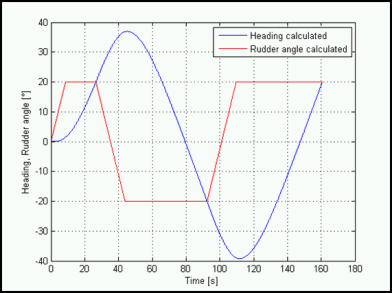
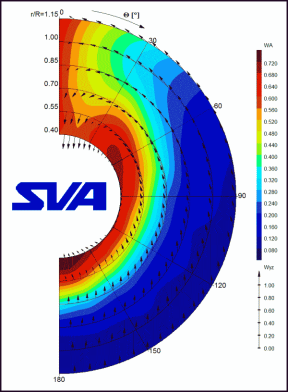
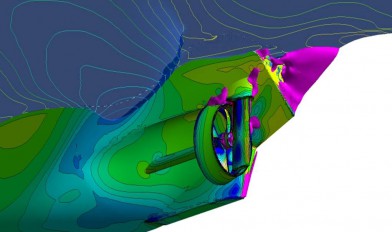
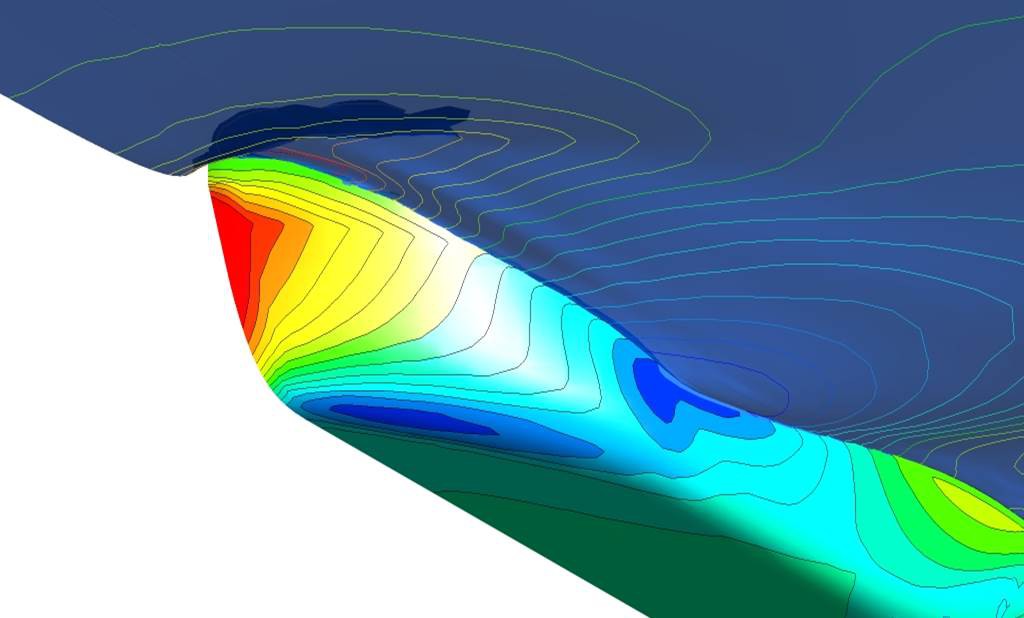
The performance prediction is the basic task of model basins.
Performance Prediction Based on Model Tests
With the aid of model tests the required propulsion power for all types of vessels is determined. The classic performance prediction is based on
- resistance tests
- open water tests
- and propulsion experiments.
As a result of these tests, all performance parameters can be identified. The extrapolation of the model test results takes place either without determining the form factor, or in accordance with the ITTC 1978 Performance Prediction Method with form factor. Both methods are well established and provide reliable results for the most cases. The SVA performs the propulsion tests by applying the British method.
Prerequisite for the extrapolation of the test results is high accuracy in measuring and in the model finish. The SVA complies with the requirements of the ITTC (International Towing Tank Conference) for all areas of the test system. Advanced measuring and analysis technology helps the test engineer and reduces the time required to carry out the tests. The experimental results and procedures are continuously verified and validated.
Performance Prediction Based on Statistical Data
Based on the SVA database and various empirical methods the SVA Potsdam is able to create a quick performance prediction [1]. This enables a first estimate of the power requirement of a watercraft in the early design stage.
Performance Prediction Based on Viscous CFD Calculations
In viscous CFD simulations (Computational Fluid Dynamics), the flow about the geometry and the resulting resistance and the wake field will be calculated in the scales of full size and / or the model scale. Based on these calculations the potential of possible improvements of the ships lines can be detected. In order to include the effect of the working propeller on the ship resistance, the propeller effect can be simulated or the real propeller geometry taken into account in further CFD calculations. From the calculated resistance within given propulsion conditions or from the calculated torque, the delivered power can be determined. If no custom propeller data is available, the polynomials of the Wageningen B-series are alternatively used for this purpose.
The performance prediction based on viscous CFD calculations [2] is for many cases an alternative to model testing, especially when only individual operating points are required. The results can still be used for general ship evaluation, motor design, and as a basis for the propeller design.
Context Related References / Research Projects
[1] Grabert, R.: Ein Verfahren zur Leistungsprognose nach Vergleichsschiffen, Schiffbauforschung 31(1992)1
[2] Rieck, K., Hellwig-Rieck, K.: Numerische Propulsionsprognose von Schiffen, STG-hauptversammlung, Rostock, November 2011